Introduction
Green skills will disrupt the world of work. From banking to business to healthcare, rapid and global adaptation to a changing environment will shift how we live and the jobs that we hold. Expert advice from organizations like the ILO, the OECD and the Department of Labor clearly indicates the growing demand and urgency for this seismic shift in purpose and process.
Regardless of one’s view on climate change, clean energy and clean manufacturing are not only better for our planet – they provide numerous economic, structural and equitable opportunities for both our young people and our communities. Are we providing pathways to help young people and our future workforce aquire the skills and dispositions needed to fill this exponential demand?
While many are working to better embed high-quality project-based learning, real-world learning and community-connected projects in K-12, we must also consider the ways in which we might point young people towards a sustainable future. This includes, but is not limited to, jobs that address and confront environmental justice, community climate challenges, sustainable supply chains and more. Schools have the power, and the responsibility, to play a guiding role in this work. United World Colleges has a great framework for what sustainability means at the level of dispositions and competencies.
Why Now?
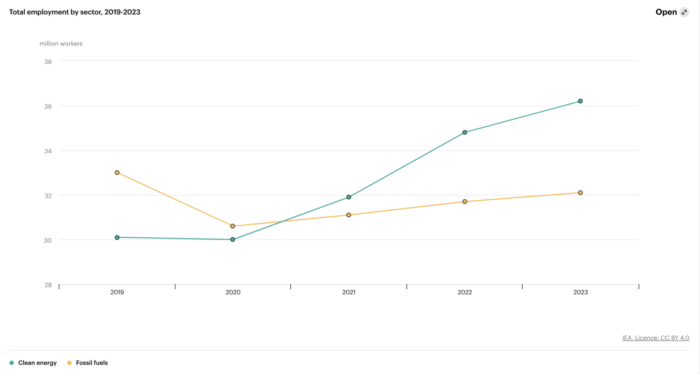
Legislation like the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) isn’t just about climate policy and incentivizing schools toward a cleaner future – it’s about jobs. A clean economy not only creates more opportunities, it also increases stability (e.g. enhancements to global supply chains) and renewed energy security. This transition towards sustainability will produce millions of well-paid jobs that have the capacity to rejuvenate our towns, reduce inequality, and revitalize communities.
Billions of dollars are being invested to help our nation make this energy transition, but at the moment we can only hope that we will have the human resources necessary to meet the demand of solar panel installation, wind turbine building and repair, materials sciences and infrastructure design and maintenance that will facilitate the transition to a greener economy.
Bill McKibben identified that “the two limiting factors of climate change will be whether we can overcome the fossil fuel industry’s meddling, and, whether we can build out above all the human capital that we need.” He then said, “I mean, the best estimate is it’s going to take at least a million more electricians in the U.S. [alone]. If you know a young person who wants to do something that’s going to help the world and wants to make a good living at the same time, tell them to go become an electrician.”
If you know a young person who wants to do something that’s going to help the world and wants to make a good living at the same time, tell them to go become an electrician.
Bill McKibben
The BlueGreen Alliance estimates over nine million jobs over the next decade alone from the IRA and other likely legislation with even higher estimates from some organizations – 23 million from the Advanced Energy Economy – that will stem from the passage of this bill. Industries include clean energy (5 million jobs), clean manufacturing (900,000), efficient buildings (900,000), natural infrastructure (600,ooo), clean transportation (400,000), and environmental justice (150,000). Indirectly we know this green transition will impact other careers like education, healthcare, law, business, and finance – everyone needs to be ready. Similarly, the Associated Builders and Contractors conducted a survey that, coupled with prospective construction data, indicates an employment gap of 546,000 construction workers in 2023 alone. A gap that must be readily filled and exceeded in order to adapt and grow American infrastructure.
Planet ED, an initiative of the Aspen Institute, published a brief on school infrastructure and CTE, making a similar call to “Invest in career and technical education programs to increase access to clean energy jobs and to integrate environmental sustainability across career pathways” and to “invest in youth to ensure an equitable and just transition.”
A recent summary of recommendations from IREC, a workforce development organization that builds the foundation for rapid adoption of clean energy and energy efficiency to benefit people, the economy, and our planet, includes: “[we must] develop and promote career pathways” and “integrate clean energy into existing education and professional development pathways.”
The green revolution is here, and legislation has created a tremendous opportunity for our students. We need to ask ourselves – are we doing what we can to facilitate this transition? Let’s help our students set foot on the right path.